What Is A Linkage And How Does It Work?
Linkages play a vital role in various engineering and power transmission applications in a range of sectors. In this article, we’ll look at what linkages are, their working mechanisms, and their potential applications in a professional context.
What Is A Linkage?
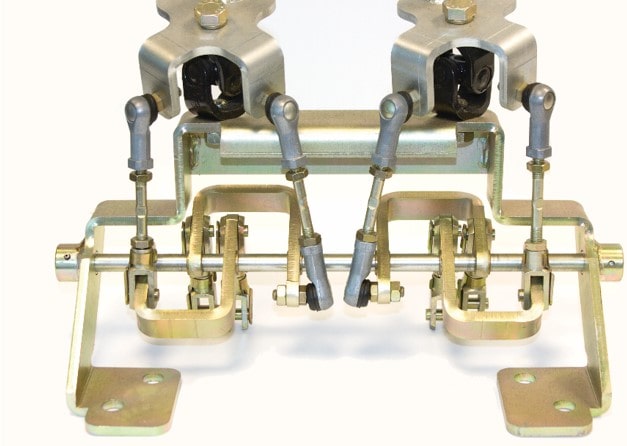
A linkage is a mechanical assembly that connects two or more components together within a system or application. Linkages have self-aligning capabilities, meaning that the components can maintain proper orientation even in the presence of external forces or misalignments. Linkages are primarily used to transfer motion between two components while reducing the impact of transmitted forces.
How Do Linkages Work?
Linkages typically consist of rods, levers, or other elements that are connected by pivots or joints. These connections allow the elements to rotate or move relative to one another while sustaining their alignment. The resulting mechanism ensures a seamless and controlled transfer of kinetic energy and motion between the ‘linked’ components.
Some common materials used for manufacturing rod-based linkages include steel, stainless steel, and aluminium. These materials offer the desired blend of strength, durability, and corrosion resistance. Various plating and coating options are also available to provide colour choices and increased corrosion resistance for specific applications.
To minimise operational friction and wear, and to suit various operating environments, liner materials can be selected based on application-specific requirements. Please get in touch with one of our experienced engineering team to find out more.
Linkage Mechanisms Explained
Linkage mechanisms typically follow three basic principles:
-
Relative motion transfer: Linkages can transfer motion between the connected components in a specified manner. This can range from simple one-to-one motion transfer to complex proportional or inverse motion transfer patterns.
-
Force distribution: By absorbing some of the applied forces, linkages can distribute the forces evenly, ensuring the stability and durability of the connected components and reducing the risk of component failure.
-
Motion control: Linkages can provide controlled motion in specific directions and can restrict unwanted motion, thus ensuring the desired motion outcome for a given application and reducing wasted energy.
Applications Of Linkages
Linkages have applications across a wide range of industries and equipment. Some of these applications include:
-
Automotive: In the automotive industry, linkages play a crucial role in suspension systems, steering mechanisms, and transmission systems.
-
Aerospace: Linkages are used in the aerospace industry for various tasks such as aircraft control surfaces, landing gear systems, and engine controls.
-
Industrial machinery: Linkages find applications in machines like presses, conveyors, and packaging equipment where precise motion and force transfer are essential.
-
Robotics: Linkages are integral to robotic arms and manipulators, enabling complex motion patterns and accurate positioning.
Next Steps
Linkages and their mechanisms provide a valuable foundation for the power transmission systems used in industrial machinery and equipment, as well as vehicles and mobile plant.
At BTL-UK, we use the latest CNC (Computer Numerical Control) precision machine tools to ensure accuracy and efficiency in the manufacturing process, creating a wide range of high-quality linkages that maximise value and operational efficiency for our customers.
To find out more or to request a quote, please click here to contact us today.






